
Overview
Season 1: Episode 3
In this episode, we discuss the Stop the Bleed program with Gina Solomon, Trauma Program Manager at Gwinnett Medical Center in Lawrenceville, Georgia. Gina shares her extensive experience in trauma care and the importance of the Stop the Bleed initiative.
Learn how Stop the Bleed, a program born out of tragic events like the Sandy Hook shooting, is designed to teach laypeople how to control bleeding in emergency situations. Gina explains the ABCs of bleeding control: Alert, Bleeding, and Compression, and emphasizes the significance of quick, decisive action to save lives.
Discover practical advice on the use of tourniquets, wound packing, and other life-saving techniques that can be applied in various scenarios, from active shooter incidents to everyday accidents. Join us as we delve into the essentials of trauma care and how you can get involved in this crucial program.
Transcript
View podcast transcript
1
00:00:00,000 –> 00:00:11,280
Music.
2
00:00:11,462 –> 00:00:15,342
Hello and welcome to another episode of the Self-Initiative Project Podcast.
3
00:00:15,862 –> 00:00:17,622
I’m your host, Jim O’Brien.
4
00:00:18,202 –> 00:00:22,642
In our third podcast, we’re going to be talking about Stop the Bleed.
5
00:00:22,682 –> 00:00:27,042
You can learn more about Stop the Bleed at bleedingcontrol.org.
6
00:00:27,262 –> 00:00:31,482
Today, we’re talking to Gina Solomon, the Trauma Program Manager at Gwinnett
7
00:00:31,482 –> 00:00:33,742
Medical Center in Lawrenceville, Georgia. How are you, Gina?
8
00:00:34,062 –> 00:00:39,022
I am good. How are you? Good. And we’re here to talk about the Stop the Bleed program.
9
00:00:39,202 –> 00:00:43,182
But before we get started on that, I want you to tell our audience a little
10
00:00:43,182 –> 00:00:46,442
bit about yourself and who you are and what your background is.
11
00:00:46,962 –> 00:00:51,202
Sure. As you said, I am the trauma program manager at Gwinnett Medical Center.
12
00:00:51,322 –> 00:00:58,642
And kind of what that is in a nutshell is I oversee the level two trauma program here at our facility.
13
00:00:58,902 –> 00:01:01,122
I’m a nurse. I’ve been a nurse for 25 years.
14
00:01:01,902 –> 00:01:07,162
Worked in critical care areas in the emergency department with a focus on the
15
00:01:07,162 –> 00:01:09,282
care of trauma patients, has kind of been my background.
16
00:01:10,322 –> 00:01:14,342
Sure, sure. So a nurse for a long time, I gather.
17
00:01:15,162 –> 00:01:19,642
Yes. Seen a lot of action, I’m sure, doing what it is you do.
18
00:01:20,642 –> 00:01:26,282
Yes, sir. Yes, sir, for sure. Well, I want to thank you for all that work that you do for us.
19
00:01:26,942 –> 00:01:29,802
So Stop the Bleed, what is this all about?
20
00:01:30,322 –> 00:01:35,542
What is this all about? Great question. It’s really this initiative that it
21
00:01:35,542 –> 00:01:42,502
has just snowballed and for good reason because it’s really life-saving and it’s very easy to learn.
22
00:01:42,562 –> 00:01:46,542
I put it in the, you know, category with CPR, you know, that we’ve just,
23
00:01:46,602 –> 00:01:49,642
you know, we’ve really pushed that out to the public that we,
24
00:01:49,702 –> 00:01:53,862
you know, anybody can learn how to do CPR and you can really make a difference.
25
00:01:54,002 –> 00:02:00,422
So Stop the Bleed is a program that’s along those lines, but it’s really about controlling bleeding.
26
00:02:01,122 –> 00:02:06,322
Back in around 2012, the program came out and unfortunately,
27
00:02:06,562 –> 00:02:12,722
it was born out of a group that got together called the Hartford Consensus that
28
00:02:12,722 –> 00:02:15,222
came together after the Sandy Hook shooting.
29
00:02:16,042 –> 00:02:17,682
Okay. So this was a group.
30
00:02:18,781 –> 00:02:22,641
Emergency management folks, EMS,
31
00:02:22,981 –> 00:02:29,021
trauma surgeons, law enforcement, to really sit down and look at not only Sandy
32
00:02:29,021 –> 00:02:37,501
Hook, but some of the other mass shooting scenarios that we had had in our country, unfortunately.
33
00:02:37,581 –> 00:02:41,641
And how could we make a difference?
34
00:02:41,941 –> 00:02:46,841
How could we decrease the loss of life in these scenarios.
35
00:02:47,681 –> 00:02:51,521
Yeah. No, I was just going to say, it’s unfortunate that, you know,
36
00:02:52,361 –> 00:02:56,601
tragedies, you know, get you to make you have to think about these sorts of things. Right.
37
00:02:56,681 –> 00:03:00,781
But the good news is, is that tragedy, sometimes a lot of good come from them.
38
00:03:00,861 –> 00:03:02,341
And I would say this is one of those things.
39
00:03:03,361 –> 00:03:06,601
Absolutely. And, you know, sometimes that’s all you, you can do is,
40
00:03:06,601 –> 00:03:11,361
is, you know, we can’t go back and undo this situation, but what can we learn
41
00:03:11,361 –> 00:03:14,761
from it? And that’s really what this group did.
42
00:03:14,981 –> 00:03:19,721
So when they sat and went back and looked at a lot of these,
43
00:03:19,881 –> 00:03:26,421
what they realized is it takes a little while for the pre-hospital responders
44
00:03:26,421 –> 00:03:29,661
to get on scene and render aid.
45
00:03:29,661 –> 00:03:34,641
There’s a lot of factors that involve that if you still have somebody who’s
46
00:03:34,641 –> 00:03:40,401
actively shooting on the scene or, you know, you don’t know what’s going on.
47
00:03:40,441 –> 00:03:45,301
The first present there is typically law enforcement and their job is to get the bad guy.
48
00:03:46,022 –> 00:03:50,982
Not necessarily to help bleeding people. You know, and that’s a good point that
49
00:03:50,982 –> 00:03:55,042
you make, because I don’t think that many people realize that when first responders
50
00:03:55,042 –> 00:03:58,842
come on the scene, at least as far as law enforcement goes or otherwise,
51
00:03:59,082 –> 00:04:02,682
they’re not there necessarily to take care of the injured. They’re there first
52
00:04:02,682 –> 00:04:04,062
to clear out the bad people.
53
00:04:04,562 –> 00:04:08,442
And so you’re left to your own demise there for a little while until they can
54
00:04:08,442 –> 00:04:12,162
get things under control and then let those pre-hospital folks in.
55
00:04:12,242 –> 00:04:16,922
And that’s the first time I’ve ever heard that said that way as well. Pre-hospital folks.
56
00:04:17,482 –> 00:04:23,262
Pre-hospital, yeah. Well, and you don’t, and you wouldn’t think about that,
57
00:04:23,382 –> 00:04:26,642
that they have to neutralize that threat.
58
00:04:26,702 –> 00:04:32,782
That is the first goal, you know, is to stop that person from injuring anybody else.
59
00:04:32,982 –> 00:04:37,422
Absolutely. So they have to neutralize that threat before they let the medical
60
00:04:37,422 –> 00:04:39,782
pre-hospital responders in.
61
00:04:40,142 –> 00:04:49,082
So there was lag time before people came in that could render aid to these folks.
62
00:04:49,162 –> 00:04:56,902
And sometimes a very long time, like with Columbine, it was hours before there
63
00:04:56,902 –> 00:05:00,682
were medical personnel allowed in the building to begin to render aid.
64
00:05:00,922 –> 00:05:06,002
And what they found was that the people that were injured,
65
00:05:06,002 –> 00:05:10,682
some of them died from just acute blood loss that could have been controlled
66
00:05:10,682 –> 00:05:16,262
by some simple maneuvers that’s easily passed on to lay people.
67
00:05:16,482 –> 00:05:20,822
So this is kind of where Stop the Bleed came out of.
68
00:05:20,942 –> 00:05:27,822
And it’s really meant it started out with law enforcement was a target for it.
69
00:05:27,842 –> 00:05:34,002
And we do teach this to law enforcement and law enforcement as well as.
70
00:05:34,707 –> 00:05:38,867
Pre-hospital medical personnel have really began to change the way that they
71
00:05:38,867 –> 00:05:40,447
respond to these events.
72
00:05:40,627 –> 00:05:43,467
And they almost do it more as a team approach.
73
00:05:43,827 –> 00:05:47,467
And that’s been one piece of it. But the other piece of it is the Stop the Bleed
74
00:05:47,467 –> 00:05:50,627
program. And that’s teaching lay people how to control hemorrhage.
75
00:05:50,847 –> 00:05:55,427
Because if you can stop the blood from coming out, you can buy folks some time
76
00:05:55,427 –> 00:06:00,807
until those pre-hospital medical responders can come in and get you out.
77
00:06:01,007 –> 00:06:05,807
And they truly believe that that can save lives in the long run. Yeah, absolutely.
78
00:06:06,127 –> 00:06:11,907
And do I remember somewhere hearing that in, you know, trauma events that bleeding
79
00:06:11,907 –> 00:06:14,567
is one of the number one causes of death?
80
00:06:14,727 –> 00:06:17,607
Am I making that up or have I heard that somewhere? Yeah, well,
81
00:06:17,607 –> 00:06:22,587
no. And actually uncontrolled hemorrhage is the leading cause of preventable death.
82
00:06:22,827 –> 00:06:26,467
Okay. You know, there are things that we cannot prevent, but if we can keep
83
00:06:26,467 –> 00:06:32,247
the blood in your body, you know, then it can buy us some time to potentially
84
00:06:32,247 –> 00:06:34,367
fix that. Kind of important.
85
00:06:35,247 –> 00:06:39,467
Right. And a lot of what we do in trauma care, we learn from the military and
86
00:06:39,467 –> 00:06:42,247
we learn from conflicts. We learn from war.
87
00:06:42,627 –> 00:06:48,267
So the use of tourniquets and all are coming out of the conflicts in the Middle
88
00:06:48,267 –> 00:06:51,167
East and they’ve learned that and they have saved numerous lives.
89
00:06:51,447 –> 00:06:56,727
You know, you can live without part of an arm or a leg, but you can’t live without your blood volume.
90
00:06:56,847 –> 00:07:04,267
So, you know, learning on ways to control that has really been important and has been huge.
91
00:07:05,007 –> 00:07:09,967
Sure. And I assume that, you know, part of this stop the bleed program is the
92
00:07:09,967 –> 00:07:12,967
use of tourniquets, right? And that’s gotta be a pretty big part.
93
00:07:13,427 –> 00:07:19,527
It is, it is a big part. It’s for arm and leg wounds. Um, it’s a large part of that.
94
00:07:19,747 –> 00:07:23,207
And then the other part of it just being, you know, compression,
95
00:07:23,367 –> 00:07:27,287
good old holding pressure and not being afraid to do that and how to do it properly.
96
00:07:27,547 –> 00:07:31,207
Yeah. Well, I, I asked about the the tourniquet thing, because I’m a big proponent
97
00:07:31,207 –> 00:07:35,387
of tourniquets and I carry at any given time, I probably have two to three in
98
00:07:35,387 –> 00:07:37,327
my bags that I have with me at any time.
99
00:07:37,847 –> 00:07:41,987
And, you know, because it’s the go-to. And, you know, having quite a bit of
100
00:07:41,987 –> 00:07:44,127
interaction with law enforcement locally lately,
101
00:07:44,307 –> 00:07:49,287
I think it’s great that most all, if not every officer now carries a tourniquet
102
00:07:49,287 –> 00:07:53,307
on their utility belt all the time just for such incidents.
103
00:07:53,587 –> 00:07:57,307
But I wanted to talk about tourniquets for a minute specifically just to dispel
104
00:07:57,307 –> 00:08:00,587
some of the rumors about tourniquets, because I think in the past,
105
00:08:00,627 –> 00:08:02,267
and I think even still now,
106
00:08:02,627 –> 00:08:06,907
there are some individuals and entities that think that tourniquets are bad
107
00:08:06,907 –> 00:08:12,147
or dangerous because it kills the local cells or, you know, you can’t get filling
108
00:08:12,147 –> 00:08:16,427
back where the tourniquet’s been applied and they’re just not ideal to use.
109
00:08:16,547 –> 00:08:20,827
Can we talk about that for a minute and maybe help dispel some of the bad juju
110
00:08:20,827 –> 00:08:22,507
and myths about tourniquets? Right.
111
00:08:23,347 –> 00:08:26,267
Absolutely. Well, you know, when when Turk is first born.
112
00:08:27,406 –> 00:08:31,706
Were used, and again, it was in a military conflict and don’t,
113
00:08:31,706 –> 00:08:40,266
you know, it was the Korea-Vietnam era type, and they were seeing a lot of amputations.
114
00:08:40,266 –> 00:08:46,426
And unfortunately, they kind of correlated the amputation rate to the tourniquet
115
00:08:46,426 –> 00:08:48,146
use that, you know, this was bad.
116
00:08:48,246 –> 00:08:53,326
And the tourniquet itself was causing the need for these amputations.
117
00:08:53,326 –> 00:09:00,306
But with the Operation Desert Storm and all this, we began back into another
118
00:09:00,306 –> 00:09:05,146
conflict and they really began to study that.
119
00:09:05,446 –> 00:09:10,246
And what they found is the complete opposite.
120
00:09:10,466 –> 00:09:16,406
Sometimes those amputations happen, but it’s really related to the damage to
121
00:09:16,406 –> 00:09:18,666
the extremity, not the use of the tourniquet.
122
00:09:18,786 –> 00:09:23,266
So tourniquets have been used in the hospital for many, many years.
123
00:09:23,386 –> 00:09:27,926
Folks that have orthopedic surgery, knee replacements, those such,
124
00:09:28,066 –> 00:09:32,606
you’ve had a tourniquet placed on your extremity for a prolonged period of time
125
00:09:32,606 –> 00:09:34,486
for them to be able to do that.
126
00:09:35,066 –> 00:09:41,806
So they’re not unusual to the hospital and haven’t been, but changing that thought
127
00:09:41,806 –> 00:09:49,726
process that the tourniquet itself causes that extreme damage and causes amputations.
128
00:09:49,726 –> 00:09:54,486
The studies have shown that no amputations have occurred due to a tourniquet
129
00:09:54,486 –> 00:09:56,826
being left on two hours or less.
130
00:09:57,146 –> 00:10:01,746
So you do with prolonged period of time with a tourniquet, you’re shutting off
131
00:10:01,746 –> 00:10:04,826
blood flow to your tissues can cause some local damage.
132
00:10:05,026 –> 00:10:11,206
But if you truly need that tourniquet, You know, we can deal with the tissue damage, but you cannot.
133
00:10:12,130 –> 00:10:17,710
Deal with extreme blood loss. So that becomes the caveat there.
134
00:10:17,930 –> 00:10:21,750
And if you see any video from,
135
00:10:22,490 –> 00:10:26,810
over in the Middle East and our military in combat situations,
136
00:10:27,250 –> 00:10:30,970
you will often see tourniquets that are already placed on their arms and legs,
137
00:10:31,130 –> 00:10:34,090
and all they have to do is tighten them because they’ve,
138
00:10:34,710 –> 00:10:38,630
really shown that they make a difference and they save lives if they can control
139
00:10:38,630 –> 00:10:44,550
that hemorrhage until they can get them to definitive care and somebody who can fix that.
140
00:10:44,950 –> 00:10:49,730
Yeah, and I had heard that as far as any type of tissue damage that might occur
141
00:10:49,730 –> 00:10:55,630
after prolonged use of a tourniquet could pretty much be fully reversed with
142
00:10:55,630 –> 00:10:57,550
medication that we have today anyway.
143
00:10:58,130 –> 00:11:01,750
It depends, and if we know, you know, we know ahead of time,
144
00:11:01,770 –> 00:11:06,790
you know, that we’ve had this tissue, there are ways that we can take the tourniquet down,
145
00:11:06,970 –> 00:11:12,530
and yes, there are medications that we can do to kind of help mitigate the return
146
00:11:12,530 –> 00:11:14,550
of blood flow to that extremity.
147
00:11:14,590 –> 00:11:19,150
Because what happens is you shut off the blood flow to that tissue and the tissue
148
00:11:19,150 –> 00:11:23,670
starts to metabolize things that are not necessarily good for the body because
149
00:11:23,670 –> 00:11:25,910
it doesn’t have its usual routes.
150
00:11:26,230 –> 00:11:28,750
You know, it’s not good enough. And then the good things that,
151
00:11:28,770 –> 00:11:29,910
you know, it needs to function.
152
00:11:30,650 –> 00:11:33,690
So there will be toxins that build up because of that.
153
00:11:33,750 –> 00:11:36,970
But there are ways to let it go, be prepared for those toxins,
154
00:11:37,070 –> 00:11:43,470
you know, when you return flow back to that extremity, you know, and if you,
155
00:11:43,630 –> 00:11:48,170
you know, heaven forbid, have an extreme case where it was left on an extremely
156
00:11:48,170 –> 00:11:52,370
long period of time, you know, they would be able to mitigate that,
157
00:11:52,570 –> 00:11:58,830
you know, with surgery, amputation, or knowing that’s going to happen as a possibility.
158
00:11:59,030 –> 00:12:05,010
But again, loss of limb is much better than loss of life, especially where we
159
00:12:05,010 –> 00:12:09,090
have come Um, technology wise with prosthetics are just absolutely amazing,
160
00:12:09,250 –> 00:12:15,210
you know, so people are returning to almost normal functioning with prosthetics.
161
00:12:15,250 –> 00:12:22,250
So, so they’re, you know, not ideal, but certainly manageable and again,
162
00:12:22,310 –> 00:12:24,230
better than the overall loss of life.
163
00:12:24,390 –> 00:12:28,730
Yeah. I think the alternative is a lot worse in the overall scheme of things.
164
00:12:28,770 –> 00:12:32,750
So tourniquets are good and they can definitely go a long way towards stopping
165
00:12:32,750 –> 00:12:37,890
severe hemorrhaging and hopefully and most likely helping to save that life.
166
00:12:38,550 –> 00:12:43,070
Absolutely. So back to Stop the Bleed. And for folks wanting to know more,
167
00:12:43,110 –> 00:12:45,570
you can learn more at bleedingcontrol.org.
168
00:12:45,650 –> 00:12:46,670
I think I got that right.
169
00:12:46,970 –> 00:12:53,470
Correct. So let’s talk about just kind of going through the outline that I have for it.
170
00:12:53,510 –> 00:12:56,550
Let’s talk about the primary principles of trauma care response.
171
00:12:57,708 –> 00:13:04,988
Yeah. Well, you know, it’s, you want to find the bleeding and control it.
172
00:13:05,028 –> 00:13:08,008
And we talk about, we like ABCs in the medical world.
173
00:13:08,248 –> 00:13:10,748
We do a lot of things based on the alphabet.
174
00:13:13,288 –> 00:13:17,408
Because people remember that they can recognize that and, you know,
175
00:13:17,488 –> 00:13:18,888
mnemonics are really easy.
176
00:13:18,988 –> 00:13:25,588
So, So, you know, it’s, hey, I noticed something is wrong. So, A, let’s alert.
177
00:13:25,808 –> 00:13:29,268
Let’s get, call 911 and get the help that we need.
178
00:13:29,868 –> 00:13:33,968
And then B is for bleeding. We need to find it. Okay, where is it coming from?
179
00:13:34,088 –> 00:13:38,408
And that may be tearing clothes, cutting clothes, because you really need to
180
00:13:38,408 –> 00:13:41,068
see where it’s coming from to be able to stop it.
181
00:13:41,208 –> 00:13:44,968
Sometimes you’ll just see somebody, you know, covered head to toe with blood.
182
00:13:45,008 –> 00:13:48,388
And that’s not really helpful because you’ve got to get to the site that it’s
183
00:13:48,388 –> 00:13:49,568
coming from. You got to find it.
184
00:13:49,708 –> 00:13:52,368
You got to find it. And then C is compress.
185
00:13:52,528 –> 00:13:57,088
And we talk about three different ways to compress. And first off is just direct
186
00:13:57,088 –> 00:14:00,988
pressure, good old direct pressure that we learn works most of the time.
187
00:14:01,968 –> 00:14:04,908
And then we have wound packing. So if you have a deep wound,
188
00:14:05,128 –> 00:14:08,968
it’s the same principle except for you’re taking that gauze or that towel or
189
00:14:08,968 –> 00:14:13,108
T-shirt and actually stuffing it into a larger wound and then holding pressure.
190
00:14:13,528 –> 00:14:17,528
And then the tourniquets is the third way to compress. So if you have uncontrolled
191
00:14:17,528 –> 00:14:19,848
hemorrhage on an arm or a leg,
192
00:14:19,948 –> 00:14:25,688
you can utilize a tourniquet to stop the flow of blood to that extremity and
193
00:14:25,688 –> 00:14:29,748
it’s not coming out of the wound at that point in time.
194
00:14:29,968 –> 00:14:33,768
So those are really the three major principles.
195
00:14:34,288 –> 00:14:37,628
They’ve kept Stop the Bleed very simple because the goal is,
196
00:14:37,648 –> 00:14:41,008
you know, that lay people can learn how to do this, you know,
197
00:14:41,008 –> 00:14:44,068
and we want to train as many people as possible.
198
00:14:44,408 –> 00:14:47,888
Absolutely. You know, like one of my coworkers says, you know,
199
00:14:47,888 –> 00:14:51,588
I want the person behind me in Walmart to know how to do this.
200
00:14:51,668 –> 00:14:56,028
You know, if if I need it, you know, if something happens, you want the person
201
00:14:56,028 –> 00:15:00,488
next to you to be able to to understand the principles and be able to render
202
00:15:00,488 –> 00:15:01,908
aid until help can arrive.
203
00:15:02,468 –> 00:15:06,188
Yeah. And, you know, it’s an important point to make because at the end of the
204
00:15:06,188 –> 00:15:08,868
day, and I think that what you were getting at earlier, too,
205
00:15:09,068 –> 00:15:14,368
we kind of wind up being or needing to be our own first responders at the end
206
00:15:14,368 –> 00:15:20,188
of the day, especially in these situations where we may be a long way away from help,
207
00:15:20,288 –> 00:15:24,808
getting help, or it takes some time to get the help that we need,
208
00:15:24,868 –> 00:15:26,568
right? We’re first on the scene.
209
00:15:26,908 –> 00:15:31,308
And really, we have a responsibility to ourselves and our loved ones to kind
210
00:15:31,308 –> 00:15:36,448
of know these sorts of things and be able to render that level of help to ourselves and those.
211
00:15:37,319 –> 00:15:41,879
Absolutely. And the other key piece of it is, you know, unfortunately,
212
00:15:42,079 –> 00:15:46,059
you know, all we have to do is turn on the news to hear of, you know,
213
00:15:46,059 –> 00:15:50,359
some unfortunate situation, you know, just another one today in Texas.
214
00:15:50,359 –> 00:15:58,959
But we see tourniquets often coming into the emergency room that have been used outside the hospital.
215
00:15:58,959 –> 00:16:01,779
And you know here in Gwinnett County there’s been
216
00:16:01,779 –> 00:16:04,739
no news report of mass shootings or bombings that people or
217
00:16:04,739 –> 00:16:08,699
motor vehicle crashes work injuries home
218
00:16:08,699 –> 00:16:11,639
injuries you know the principles of this
219
00:16:11,639 –> 00:16:15,639
we are training teachers in schools and there was just a school teacher in the
220
00:16:15,639 –> 00:16:20,719
neighboring county who used one on a on a child who fell off playground equipment
221
00:16:20,719 –> 00:16:27,159
and severely broke her arm and it cut an artery in her arm the bone bit so she
222
00:16:27,159 –> 00:16:28,799
was able to control that bleeding.
223
00:16:29,459 –> 00:16:33,739
Yeah, you know, like we were talking about earlier, this program was born out
224
00:16:33,739 –> 00:16:37,619
of, you know, active shooter scenarios, tragedy at Sandy Hook.
225
00:16:37,759 –> 00:16:42,079
But the reality of it is an accident to cause severe hemorrhaging can happen
226
00:16:42,079 –> 00:16:48,039
any place, anytime. I saw a fantastic meme on one of the social media outlets
227
00:16:48,039 –> 00:16:52,279
earlier just this week, and it was a picture of a big chainsaw.
228
00:16:52,439 –> 00:16:56,599
And it was to remind you that, you know, tourniquets don’t just have use on
229
00:16:56,599 –> 00:16:59,519
the battlefield or in these tragic scenarios.
230
00:17:00,159 –> 00:17:03,719
It could be in your backyard, you know? Absolutely.
231
00:17:03,959 –> 00:17:08,379
Absolutely. One of the places that I carry my trauma kits is in the gun range
232
00:17:08,379 –> 00:17:12,219
because I’ve worked up until recently. I’ve done some work as a range safety
233
00:17:12,219 –> 00:17:15,239
officer and I, I shoot fairly regularly.
234
00:17:15,279 –> 00:17:21,199
So I always am sure to have a kit in there if nowhere else, because even if
235
00:17:21,199 –> 00:17:24,759
something doesn’t happen to you, you see sometimes some pretty silly,
236
00:17:24,839 –> 00:17:28,639
unsafe things going on. So it can happen anywhere.
237
00:17:29,259 –> 00:17:33,819
Correct. And we have, we have trained one of our local gun clubs on,
238
00:17:33,839 –> 00:17:38,199
on stop the bleed, you know, the personnel that work there. So it is certainly
239
00:17:38,199 –> 00:17:43,239
useful outside of, you know, those obvious horrible tragedies that we see.
240
00:17:43,579 –> 00:17:47,699
Yeah. And keeping it simple, something like the ABCs of bleeding just makes
241
00:17:47,699 –> 00:17:52,539
it all the more easier for the masses to get the information and to learn it.
242
00:17:52,579 –> 00:17:54,299
Because it’s really not that hard, to your point.
243
00:17:54,679 –> 00:18:02,199
Right. So let’s talk about compression and what to do with that and what not to do with that.
244
00:18:02,339 –> 00:18:06,019
Okay. I think a lot of times I know I’ve done it with injuries to myself.
245
00:18:06,199 –> 00:18:09,699
You know, has it stopped bleeding? I want to lift it up and look and see if
246
00:18:09,699 –> 00:18:11,199
it’s still gushing or not.
247
00:18:11,259 –> 00:18:14,079
And then go, oh, shoot, I got to get another bandage to put back on there.
248
00:18:14,899 –> 00:18:16,339
Exactly. Things not to do.
249
00:18:17,359 –> 00:18:21,999
Right. Right. Those are things. And yes, compression, holding, direct pressure.
250
00:18:22,039 –> 00:18:26,399
That is, you know, most of the time will control most hemorrhage.
251
00:18:26,599 –> 00:18:32,039
But if you have somebody who has severe hemorrhage, you’re going to want to take medication.
252
00:18:32,539 –> 00:18:37,799
You know, of course, gauze, nice, clean gauze is great if you have it readily available.
253
00:18:38,219 –> 00:18:42,219
But if you don’t, use what you’ve got. I have a great T-shirt from the American
254
00:18:42,219 –> 00:18:45,139
College of Surgeons that says this shirt can save your life, you know.
255
00:18:45,159 –> 00:18:48,399
And the whole guise behind that is, you know, use what you have.
256
00:18:48,479 –> 00:18:52,699
It doesn’t have to be medical gauze. It can be a towel out of your car or the
257
00:18:52,699 –> 00:18:53,919
T-shirt that you have on.
258
00:18:54,239 –> 00:18:57,699
You’ve just got to get something on the wound and hold pressure.
259
00:18:57,699 –> 00:19:02,739
The best way to hold pressure is with the heel of your hand and then on a firm
260
00:19:02,739 –> 00:19:07,239
surface, because then you’re able to get, you know, good compression of the
261
00:19:07,239 –> 00:19:10,079
vessels, which is what you’re trying to do to stop the bleeding.
262
00:19:10,379 –> 00:19:11,559
And then you don’t want to peek.
263
00:19:11,959 –> 00:19:15,459
It’s very tempting. Don’t peek. I know, right? You know, it’s not Christmas.
264
00:19:15,939 –> 00:19:19,139
You know, you don’t want to peek because once you let off that compression,
265
00:19:19,379 –> 00:19:23,999
you allow it to begin to bleed again. So if you have severe hemorrhage and you
266
00:19:23,999 –> 00:19:28,659
hold pressure on it and you’re going to hold it until you’re relieved by the
267
00:19:28,659 –> 00:19:30,419
medical responders to get there.
268
00:19:30,499 –> 00:19:35,819
And it’s also really important not to, hey, the ambulance is pulled up so I can let go and walk away.
269
00:19:35,999 –> 00:19:40,759
You want to keep holding pressure until somebody takes over for you from that standpoint.
270
00:19:41,039 –> 00:19:49,239
But firm, constant pressure without looking is the best way to compress.
271
00:19:49,239 –> 00:19:53,099
Press yeah to your point you don’t have to have medical equipment either like
272
00:19:53,099 –> 00:19:56,759
we’re talking about you can use a towel out of your trunk or t-shirt off your
273
00:19:56,759 –> 00:20:01,239
back i ideally clean but again if it’s a life-threatening hemorrhage it doesn’t
274
00:20:01,239 –> 00:20:03,419
really matter just get something on there and hold it.
275
00:20:03,899 –> 00:20:08,759
Exactly we have antibiotics so we’ll take care of whatever you know we’ll figure
276
00:20:08,759 –> 00:20:12,359
all that dirty in the in the trunk of your car we’ll deal with the funk later
277
00:20:12,359 –> 00:20:18,679
yeah exactly yeah so this tourniquet versus packing, you know, sometimes,
278
00:20:18,959 –> 00:20:24,519
especially being lay person, I don’t really know when to use a tourniquet versus
279
00:20:24,519 –> 00:20:30,899
when I need to stuff a hole that’s inordinate amount of liquid that I need coming out.
280
00:20:30,999 –> 00:20:36,719
Let’s talk about when to use a tourniquet or where to use a tourniquet versus packing a wound.
281
00:20:37,019 –> 00:20:41,859
Right. Well, and it really may be an escalation for you.
282
00:20:41,899 –> 00:20:47,819
Now, obviously, the tourniquets, you need a wound that’s on an arm or a leg to be able to use that.
283
00:20:48,059 –> 00:20:51,159
So it’s really nice that that is an option.
284
00:20:51,399 –> 00:20:57,959
So, you know, if the wound is on the neck or at the shoulder or the groin,
285
00:20:58,099 –> 00:21:02,539
obviously that takes tourniquet out and wound packing, you know, may be your only option.
286
00:21:03,059 –> 00:21:10,379
But if you see loss of all or part of an arm or a leg, if you have blood spurting
287
00:21:10,379 –> 00:21:12,979
out of a wound, And that’s exactly what it looks like.
288
00:21:12,999 –> 00:21:16,519
If you cut an artery, it’s like getting a split in a garden hose.
289
00:21:16,999 –> 00:21:21,199
That’s exactly what it’s like. You know, it’s a geyser. So when I say spurting,
290
00:21:21,219 –> 00:21:22,459
that’s exactly what it does.
291
00:21:22,599 –> 00:21:27,299
Or you have blood that is constantly coming out of a wound that will not stop.
292
00:21:27,379 –> 00:21:31,059
And it’s, you know, soaking the clothes and the ground.
293
00:21:32,170 –> 00:21:36,750
So those are kind of what we consider that life-threatening hemorrhage.
294
00:21:36,970 –> 00:21:41,950
So if it’s on an arm or leg and you have a tourniquet available and it meets
295
00:21:41,950 –> 00:21:46,290
some of those things, then you can go straight to the use of the tourniquet for that.
296
00:21:47,090 –> 00:21:51,730
It’s just a Velcro band. So when you take it out of the packaging,
297
00:21:51,970 –> 00:21:57,450
you just unfold it, put it two to three inches above the site of the bleeding.
298
00:21:57,570 –> 00:21:59,310
You just want to make sure you don’t go on a joint.
299
00:21:59,670 –> 00:22:03,210
So it should be above a joint. You can put it on top of clothing.
300
00:22:03,350 –> 00:22:07,410
You just don’t want to put it on top of something bulky in a pocket or such
301
00:22:07,410 –> 00:22:11,370
as that because you want to get it snug next to the skin.
302
00:22:11,710 –> 00:22:17,130
It doesn’t even have to be extremely tight with the Velcro because you’re going
303
00:22:17,130 –> 00:22:19,570
to notice it’s a Velcro band. There’s a rod.
304
00:22:20,270 –> 00:22:25,450
We call it a windlass rod and a clip. Those are really the three parts to the tourniquet. up.
305
00:22:25,630 –> 00:22:31,590
So you use the Velcro snugly around the arm or leg, and then you take the rod
306
00:22:31,590 –> 00:22:33,910
and you turn it, and it doesn’t matter which way.
307
00:22:35,050 –> 00:22:38,630
Clockwise, counterclockwise, either way works. And you’re just going to turn
308
00:22:38,630 –> 00:22:43,650
that rod, and it’s probably going to take both hands until you can’t turn it
309
00:22:43,650 –> 00:22:48,730
anymore or you see the blood stopping from coming out of the wound.
310
00:22:48,930 –> 00:22:52,870
And then the clip is just to hold that rod that you’ve tightened in place,
311
00:22:53,030 –> 00:22:55,090
and it doesn’t allow it to unwind.
312
00:22:55,530 –> 00:22:59,830
And those are really the three key pieces to the tourniquet itself.
313
00:23:00,510 –> 00:23:05,370
So it’s quick, it’s easy to use, you can do it one-handed, so you could do it on yourself.
314
00:23:06,890 –> 00:23:13,210
And it’s designed that way to be easy to use, because you want to be able to do it quickly.
315
00:23:14,630 –> 00:23:17,190
And aren’t the tourniquets, at least the ones I’m thinking of,
316
00:23:17,190 –> 00:23:20,810
of the, what is it, the combat application tourniquet, the CATS,
317
00:23:20,810 –> 00:23:25,590
which seemed to be the go-to for everyone, the one that seems to be recommended,
318
00:23:25,890 –> 00:23:28,050
there’s a way to write the time on there.
319
00:23:28,170 –> 00:23:32,190
So first responders have some sense of when the tourniquet got applied.
320
00:23:32,230 –> 00:23:35,650
So, you know, better how you might need to.
321
00:23:36,070 –> 00:23:42,490
Yes, they do. There is a little piece of Velcro right at the clip where you can put over the clip.
322
00:23:42,570 –> 00:23:45,790
And, you know, if you had something available, Right. What time that you put it on.
323
00:23:45,810 –> 00:23:49,070
And that just lets us know at the trauma center, you know, what time it got
324
00:23:49,070 –> 00:23:51,670
put on, how long it’s been on from that standpoint.
325
00:23:51,870 –> 00:23:57,130
And it’s really important. I mean, they are very useful tools and they work
326
00:23:57,130 –> 00:23:58,230
well, but they’re painful.
327
00:23:58,710 –> 00:24:02,590
So when you’re putting a tourniquet on somebody, you’re also explaining,
328
00:24:02,650 –> 00:24:04,430
I know this hurts really, really bad.
329
00:24:05,767 –> 00:24:09,747
But, you know, I’m trying to save your life here. I’ve got to get this bleeding under control.
330
00:24:09,827 –> 00:24:13,947
But knowing that it’s painful for the person that you’re putting it on. But you can’t be afraid.
331
00:24:14,227 –> 00:24:19,607
You’ve got to tighten it, know it’s going to hurt, and just try to explain that to the patient.
332
00:24:19,687 –> 00:24:22,327
Know that your goal is to save a life.
333
00:24:22,647 –> 00:24:26,367
At least the pain lets you know that you’re alive. So let’s get through this, right?
334
00:24:27,227 –> 00:24:32,287
Exactly, exactly. Exactly. So some of the kind of pitfalls with the use of tourniquets
335
00:24:32,287 –> 00:24:38,947
is not using one, you know, being afraid to use one, not making it tight enough
336
00:24:38,947 –> 00:24:41,147
because you’re afraid you’re going to hurt somebody.
337
00:24:41,247 –> 00:24:46,547
So you really have to make it tight enough that you’re stopping all blood flow to that extremity.
338
00:24:47,167 –> 00:24:50,047
You can actually use two tourniquets if need be.
339
00:24:50,107 –> 00:24:53,547
So if you put one on and it doesn’t seem to be controlling it,
340
00:24:53,587 –> 00:24:58,887
you can put another tourniquet on above the first one so those are just some
341
00:24:58,887 –> 00:25:03,287
you know some common things that you know,
342
00:25:04,087 –> 00:25:06,927
yeah and much like lifting the compression off to look
343
00:25:06,927 –> 00:25:10,667
you don’t want to take if you do have to use two tourniquets because bleeding’s
344
00:25:10,667 –> 00:25:14,627
not slowing down to the degree that you were hoping you’d want to if you do
345
00:25:14,627 –> 00:25:18,347
get that second one on you want to go above the first one and then don’t mess
346
00:25:18,347 –> 00:25:23,007
with the first one right correct correct you don’t don’t take anything down
347
00:25:23,007 –> 00:25:24,407
and you don’t want to loosen it.
348
00:25:24,467 –> 00:25:28,547
Once you’ve put that tourniquet on, you just leave it. We’ll deal with it at the hospital.
349
00:25:28,727 –> 00:25:32,967
So, you know, you’re not going to take it down no matter if they tell you it’s
350
00:25:32,967 –> 00:25:34,707
killing them and beg you to.
351
00:25:34,807 –> 00:25:38,367
You’ve got, once you put it on, you just leave it alone. You don’t loosen it or take it off.
352
00:25:39,147 –> 00:25:42,587
And is, are the cat tourniquets really the go-to standard?
353
00:25:42,747 –> 00:25:47,307
I know there’s two or three types. It seems like I’ve seen recently there’s a newer one out.
354
00:25:47,427 –> 00:25:52,927
I know there’s the rat cat as well, rapid application, I think, is that what they call?
355
00:25:53,987 –> 00:26:00,127
What’s your preference? What do you tell folks? Yeah, there are other tourniquets out there.
356
00:26:00,267 –> 00:26:05,487
But the good thing about the cat or the combat application tourniquet is it’s
357
00:26:05,487 –> 00:26:06,867
not terribly expensive.
358
00:26:07,907 –> 00:26:09,967
It’s easy to use. Okay.
359
00:26:10,700 –> 00:26:14,780
And, you know, those are the two main things about that.
360
00:26:14,920 –> 00:26:18,720
So the cat tourniquet actually is the preferred military tourniquet.
361
00:26:19,200 –> 00:26:24,060
So, again, they’re the ones that, you know, that we’ve learned a lot about this
362
00:26:24,060 –> 00:26:25,620
tourniquet. So we know that it works.
363
00:26:26,280 –> 00:26:30,120
So that’s kind of what we see the most of is the cat tourniquet. Sure.
364
00:26:30,740 –> 00:26:33,540
Yeah. And you want to be careful. You can get them pretty easily.
365
00:26:33,580 –> 00:26:34,820
You can get them off Amazon.
366
00:26:35,040 –> 00:26:42,300
They run around $25, $26. I think the new Gen 7 is somewhere around $27,
367
00:26:42,480 –> 00:26:44,640
$28, but you can get them off of Amazon.
368
00:26:44,980 –> 00:26:48,760
But what you want to be careful of is some of the Chinese knockoffs where you’re
369
00:26:48,760 –> 00:26:50,760
getting a three-pack for $14.
370
00:26:50,980 –> 00:26:56,720
You want to save your pennies and spend the extra $10 and get an authentic cat.
371
00:26:57,060 –> 00:27:02,120
Absolutely, because North American Rescue is the only company making the authentic
372
00:27:02,120 –> 00:27:03,440
cat tourniquets right now.
373
00:27:03,760 –> 00:27:10,140
So, you know, they are ranging anywhere from $25 to $30. So if you’re not paying
374
00:27:10,140 –> 00:27:14,220
that, if you’re getting it for $9.99, it’s probably not real.
375
00:27:16,280 –> 00:27:21,620
Because understand that there are some role player and cost players who will
376
00:27:21,620 –> 00:27:25,140
wear just for looks. They’re not functional.
377
00:27:25,340 –> 00:27:29,440
And you may get something like that. And when you need it, it’s not the time
378
00:27:29,440 –> 00:27:33,000
to realize that yours is not really a real tourniquet.
379
00:27:33,420 –> 00:27:35,500
I have to ask. I’m sorry.
380
00:27:35,960 –> 00:27:40,480
Oh, no. No, I was just saying it is really important to make sure you’ve gotten an authentic one.
381
00:27:40,680 –> 00:27:44,700
I have to ask, I see these blue trainer tourniquets, and I know that’s just
382
00:27:44,700 –> 00:27:50,740
to differentiate them from the others, and probably because they get reused in training.
383
00:27:50,860 –> 00:27:54,160
You don’t want to reuse a tourniquet because it gets stretched out,
384
00:27:54,240 –> 00:27:57,080
but likely because it’s dirty and contaminated as well.
385
00:27:57,220 –> 00:28:02,900
But is there any real difference between the blue and a normal, let’s say?
386
00:28:02,900 –> 00:28:06,280
No, if you, if you had a blue tourniquet in a, in a package,
387
00:28:06,500 –> 00:28:11,120
you know, it works the same way, but they are just the, the blue is kind of
388
00:28:11,120 –> 00:28:14,700
hallmarks that this is a training tourniquet because you do,
389
00:28:14,740 –> 00:28:18,960
you know, we’ve all had Velcro that no longer Velcros, as I call it,
390
00:28:18,960 –> 00:28:21,080
you know, it’s just worn itself out.
391
00:28:21,080 –> 00:28:25,780
And that’s what happens after, you know, using a tourniquet repeatedly for training
392
00:28:25,780 –> 00:28:30,400
is you have the potential for failure there with the Velcro.
393
00:28:30,440 –> 00:28:34,200
So that’s why we recommend, you know, you don’t want a tourniquet that you might
394
00:28:34,200 –> 00:28:38,200
use on somebody you don’t want to utilize to train with or practice with or,
395
00:28:38,220 –> 00:28:43,300
you know, open and close too much because you run the risk of causing failure.
396
00:28:44,369 –> 00:28:49,049
Don’t want that. Defeats the purpose. So I think, you know, compression on a
397
00:28:49,049 –> 00:28:53,969
wound, holding constant, steady, good, solid pressure on a hemorrhage is easy
398
00:28:53,969 –> 00:28:55,009
enough and pretty straightforward.
399
00:28:55,069 –> 00:28:59,309
And even going back to first aid that I learned in the Boy Scouts, that was the go-to.
400
00:28:59,489 –> 00:29:05,089
Apply a direct, firm pressure, right? And I think with a little bit of familiarization
401
00:29:05,089 –> 00:29:11,809
with the tourniquet, folks can learn and figure out how to use one fairly easy
402
00:29:11,809 –> 00:29:13,349
because they are fairly straightforward.
403
00:29:13,349 –> 00:29:16,389
Forward and obviously it’s only appropriate for
404
00:29:16,389 –> 00:29:19,149
arms and legs but let’s talk about this
405
00:29:19,149 –> 00:29:23,269
next one because this one kind of i’m sure gives folks the heebie-jeebies where
406
00:29:23,269 –> 00:29:28,009
you got to get in there and you know we call it packing the wound but at the
407
00:29:28,009 –> 00:29:32,589
end of the day you got to get in there and stuff some stuff inside there so
408
00:29:32,589 –> 00:29:38,349
exactly if if you have a wound that’s that’s large and deep or,
409
00:29:38,549 –> 00:29:43,349
you know, a wound that may be on, like I said, the groin or the armpit or the neck.
410
00:29:43,469 –> 00:29:48,169
There are large vessels that run through there and you can’t use a tourniquet on it.
411
00:29:48,249 –> 00:29:53,749
So you may need to actually get in there because you want to get the site of the bleeding.
412
00:29:53,929 –> 00:29:58,949
And the most severe bleeding is maybe not those superficial vessels on top.
413
00:29:59,209 –> 00:30:02,329
So you want to be able to get down to the source of bleeding.
414
00:30:02,509 –> 00:30:05,429
So if you have a large, deep wound, you want to take your
415
00:30:05,429 –> 00:30:08,789
gauze or towel or t-shirt or whatever you’re using
416
00:30:08,789 –> 00:30:12,669
and actually stuff it into the wound because you really want to get down to
417
00:30:12,669 –> 00:30:17,989
the site of the bleeding so you’re just going to stuff your stuff and then you’re
418
00:30:17,989 –> 00:30:23,249
going to hold pressure on top of that if you still see bleeding coming through
419
00:30:23,249 –> 00:30:25,729
that packing you don’t want to.
420
00:30:26,446 –> 00:30:30,546
Take that packing out. You just want to add to it. So add another towel to it,
421
00:30:30,586 –> 00:30:33,966
add another roll of gauze, and again, just hold pressure.
422
00:30:34,226 –> 00:30:37,586
But it does, you know, people don’t want to, you know, non-medical people especially
423
00:30:37,586 –> 00:30:42,486
don’t want to stick their hands down or, you know, you’re worried about causing
424
00:30:42,486 –> 00:30:46,966
further damage, but you’ve got to get down in there to the main sources of bleeding.
425
00:30:47,146 –> 00:30:50,086
You know, and the deeper you go, the bigger the vessels are.
426
00:30:50,206 –> 00:30:53,566
So you’ve got to get control of those larger vessels.
427
00:30:54,506 –> 00:30:57,846
So that’s where the wing packing really comes in handy.
428
00:30:58,266 –> 00:31:03,586
Yeah. So it’s a good idea if you do have trauma kits to probably have yourself
429
00:31:03,586 –> 00:31:08,086
a set of gloves in the mix to, to protect yourself.
430
00:31:08,146 –> 00:31:13,206
But if not, if you got to go, you got to go and get that stuffing in there.
431
00:31:13,726 –> 00:31:20,886
So just to re go back over some of these again, in summary of the ABCs is after
432
00:31:20,886 –> 00:31:25,386
you’ve made sure the area is safe and you’re safe, alert, right?
433
00:31:25,486 –> 00:31:29,026
Call 911. That’s the first step. And if you can’t do it because you’ve already
434
00:31:29,026 –> 00:31:33,886
gone to work on whoever, have somebody nearby if they’re available, do it for you. Right.
435
00:31:33,986 –> 00:31:39,566
And one of the things we say about that is be bossy.
436
00:31:39,606 –> 00:31:44,306
You know, if you’re at a scene where there’s lots going on and you you have
437
00:31:44,306 –> 00:31:48,146
lots of people, you know, and you just yell, call 9-1-1, you know,
438
00:31:48,166 –> 00:31:49,846
one or two things going to happen.
439
00:31:49,886 –> 00:31:54,046
Either everybody’s going to do it and clog up 9-1-1 or nobody’s going to do
440
00:31:54,046 –> 00:31:56,666
it because they think that, you know, the next person is doing it.
441
00:31:56,746 –> 00:31:59,826
So, you know, being bossy and actually pointing somebody else,
442
00:31:59,926 –> 00:32:04,746
will you, you please call 9-1-1 can be very helpful in those kinds of scenarios.
443
00:32:05,126 –> 00:32:08,746
That’s a good point. Being very specific in those directions, those
444
00:32:08,746 –> 00:32:15,066
instructions you’re giving the next one during that chaos i think actually i
445
00:32:15,066 –> 00:32:21,506
appreciate you know somebody giving them direct instructions yeah so good point
446
00:32:21,506 –> 00:32:25,906
b obviously is for bleeding but not in the sense.
447
00:32:26,866 –> 00:32:31,886
Just finding where the bleeding the source of the bleeding is and to your point
448
00:32:31,886 –> 00:32:34,826
that could be you know if someone’s covered in blood that could be anywhere
449
00:32:34,826 –> 00:32:38,346
so you know you’re likely going to have to remove some clothing,
450
00:32:38,446 –> 00:32:41,686
lift up some clothing, or cut some clothing off to get to it.
451
00:32:42,146 –> 00:32:46,626
Correct. Great. You want to find out where it’s coming from because you can’t
452
00:32:46,626 –> 00:32:48,486
compress if you don’t know where it’s coming from.
453
00:32:48,726 –> 00:32:53,146
Yeah. And then, of course, C that we’ve spent some time on is for compression,
454
00:32:53,306 –> 00:32:57,526
applying that pressure to stop the bleeding, either by covering the wound and
455
00:32:57,526 –> 00:33:00,086
applying constant steady pressure,
456
00:33:00,426 –> 00:33:04,666
using a tourniquet if need be, or if you’ve got to get get in there and stuff
457
00:33:04,666 –> 00:33:08,146
that wound, pack that wound, in which case you’re actually still going to use
458
00:33:08,146 –> 00:33:10,646
compression when you get through packing on top of that.
459
00:33:10,786 –> 00:33:14,786
Correct. Correct. So it’s a twofold process. Great.
460
00:33:15,679 –> 00:33:18,919
Well, what can we do? What can we do to get involved? Where do I go to learn
461
00:33:18,919 –> 00:33:21,559
more and what do I need to do to sign up?
462
00:33:22,059 –> 00:33:29,399
Well, you can look at the bleedingcontrol.org has a place you can go there and
463
00:33:29,399 –> 00:33:32,219
look if people are having public classes.
464
00:33:32,379 –> 00:33:37,859
But you can reach out to your local trauma center if you know where that is.
465
00:33:37,919 –> 00:33:41,879
Just about every trauma center in the country is participating in this initiative,
466
00:33:41,959 –> 00:33:45,539
as well as our pre-hospital cohorts.
467
00:33:45,679 –> 00:33:49,599
So, you know, reach if you can get to somebody in a trauma program somewhere,
468
00:33:49,659 –> 00:33:52,859
they can usually point you to the direction to get training in.
469
00:33:52,879 –> 00:33:55,639
And, you know, like I said, we’ve trained schools.
470
00:33:55,919 –> 00:33:59,959
We’ve been to, you know, community outreach programs.
471
00:34:00,399 –> 00:34:04,799
We’ve done, you know, just drive by training, you know, here at the hospital,
472
00:34:04,919 –> 00:34:09,799
you know, set up a station and just train people as they, you know, come by.
473
00:34:09,939 –> 00:34:14,179
Because it is, you know, there’s a whole PowerPoint and everything that goes with it.
474
00:34:14,199 –> 00:34:19,039
And that’s great. But you can also train people, you know, on on the skills very quickly.
475
00:34:19,139 –> 00:34:25,799
It doesn’t take that long to do. We’ve set up at the one of the baseball fields
476
00:34:25,799 –> 00:34:28,079
in the area, train people as they come by.
477
00:34:28,139 –> 00:34:33,119
So, you know, if if you’re looking for a program, those are some suggestions
478
00:34:33,119 –> 00:34:36,579
to outreach to find people who could can come teach groups.
479
00:34:36,579 –> 00:34:40,919
Groups and and so bleedingcontrol.org has
480
00:34:40,919 –> 00:34:43,679
some information but your local trauma centers and your
481
00:34:43,679 –> 00:34:46,539
hospitals can get you hooked up with the program yes
482
00:34:46,539 –> 00:34:52,519
yes let’s talk about gear i know bleedingcontrol.org also sells some rescue
483
00:34:52,519 –> 00:34:58,559
trauma packs are there any other sources or entities that you recommend people
484
00:34:58,559 –> 00:35:06,159
looking to to get good gear from yes there there are a lot of yes bleeding Leadingcontrol.org,
485
00:35:06,179 –> 00:35:09,879
you know, has a little store on there, but there are a lot of companies,
486
00:35:10,019 –> 00:35:14,019
you know, Google can find you lots of things, you know, just make sure that
487
00:35:14,019 –> 00:35:17,659
it’s a reputable company that sells medical equipment.
488
00:35:17,879 –> 00:35:22,319
You can trust them pretty well. I know there’s a, you know, right here in Marshall,
489
00:35:22,399 –> 00:35:27,479
Georgia, there’s a local company that we’ve worked with that sell individual kits.
490
00:35:27,759 –> 00:35:31,839
And we’re also working on placing these kits like we place AEDs.
491
00:35:31,839 –> 00:35:37,879
So right in our area, we’ve placed kits at the local mall, one of the colleges.
492
00:35:38,199 –> 00:35:42,939
Minor league baseball stadium, you know, places where people may gather.
493
00:35:43,039 –> 00:35:48,299
We’ve put, we call them wall kits, where there’s actually 10 individual bleeding control kits in them.
494
00:35:48,359 –> 00:35:55,799
So the goal really is to make the tools needed to do this more readily accessible to people.
495
00:35:55,799 –> 00:36:01,619
Yeah, it’d be great if they’d make the excessive bleeding kits required like
496
00:36:01,619 –> 00:36:05,859
they do the first aid and AEDs in the corporate world as well.
497
00:36:06,039 –> 00:36:07,899
Right. And we’re working on that.
498
00:36:09,499 –> 00:36:11,319
Yeah, yeah. Baby steps.
499
00:36:13,879 –> 00:36:19,199
Well, this has been great. This is a lot of good information that I hope people can benefit from.
500
00:36:19,339 –> 00:36:22,179
It’s pretty straightforward. The ABCs of bleeding.
501
00:36:23,939 –> 00:36:28,239
Yeah, we appreciate you being on today with us. Well, I appreciate it.
502
00:36:29,680 –> 00:36:58,165
Music.
Related Content

Overview Season 1: Episode 3 In this episode, we discuss the Stop the Bleed program with Gina Solomon, Trauma Program Manager at Gwinnett Medical Center in Lawrenceville,…
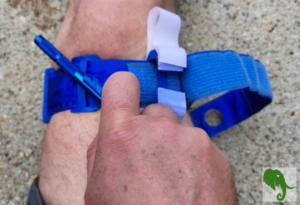
The Essential Guide to Tourniquets
Tourniquets are vital tools in emergency medical situations, particularly when dealing with severe bleeding. Understanding their use and the best practices can make a life-saving…

Building a Comprehensive Trauma Kit for Emergencies
In times of crisis or accidents, being equipped with the right tools can make the difference between life and death. Whether you’re out in the…

Listen to other episodes of the OwnGuard Solutions Podcast
Listen to our other podcasts centered around being safer and better prepared.

